Addition and Multiplication Theorems of Probability
Addition and Multiplication Theorems of Probability: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Addition Theorem of Probability, Addition Theorem of Probability for Mutually Exclusive Events,B &C etc.
Important Questions on Addition and Multiplication Theorems of Probability
The probability of solving a problem in Mathematics by two students and are and , respectively. If both of them try to solve the problem independently, then the probability that the problem will be solved by exactly one of them is equal to
M and N are any two events. The probability, that exactly one of them occurs, is
For three events, and (Exactly one of or occurs)
(Exactly one of or occurs)
(Exactly one of or occurs) and (All the three events occur simultaneously)
Then the probability that at least one of the events occurs, is:
If and are two events such that , then the incorrect statement amongst the following statements is :
and are two independent events such that and Then, is
A bag contains 5 white and 3 black balls. Two balls are drawn at random without replacement. Determine the probability of getting both the balls black.
Three faces of a fair die are yellow, two faces red and one blue. The die is thrown twice. The probability that throw will give an yellow face and the second a blue face is
There are 6 red and 5 black balls in a bag. Two balls are drawn at random one after another with replacement. The probability that both the balls drawn may be red is
If the probability for to fail in an examination is 0.2 and that for is 0.3, then the probability that either fails, is
Three persons P, Q and R independently try to hit a target. If the probabilities of their hitting the target are and respectively, then the probability that the target is hit by P or Q but not by R is:
A fair dodecahedral die numbered and is thrown and the number noted.
The events , "thrown an odd number", and , "throw an event number ", are represented on the venn diagram below:
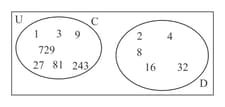
Hence show that
A fair decahedral die numbered is thrown and the number noted.
The events , 'throw a square number", and , 'throw a factor of six, are represented on the Venn diagram below:
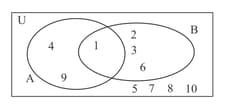
Hence show that
A coin is tossed times. The probability of getting head at least once is greater than then find the least value of
There are laddus, mangoes and samoshas in a sweets box. If Item is picked at random, What is the probability of having either a laddu or a mango ?
speaks truth in of the cases and in , cases. What is the probability that their statements about an incident do not match?
If and , then value of is
There are two bags, bag contains white and red balls and bag contains white and red balls. A ball is drawn randomly from bag and put in bag Now balls are drawn from bag and found to be red. Then the probability that white ball was drawn from bag to bag is
If and are exhaustive events satisfying , and then is equal to
A fair coin is tossed until one of the sides occurs twice in a row. Probability that even number of tosses required is
Let and are the probabilities of a student passing three independent exams and respectively. If and are the roots of equation , then the probability that the student passes in exactly one of and is
